Introduction
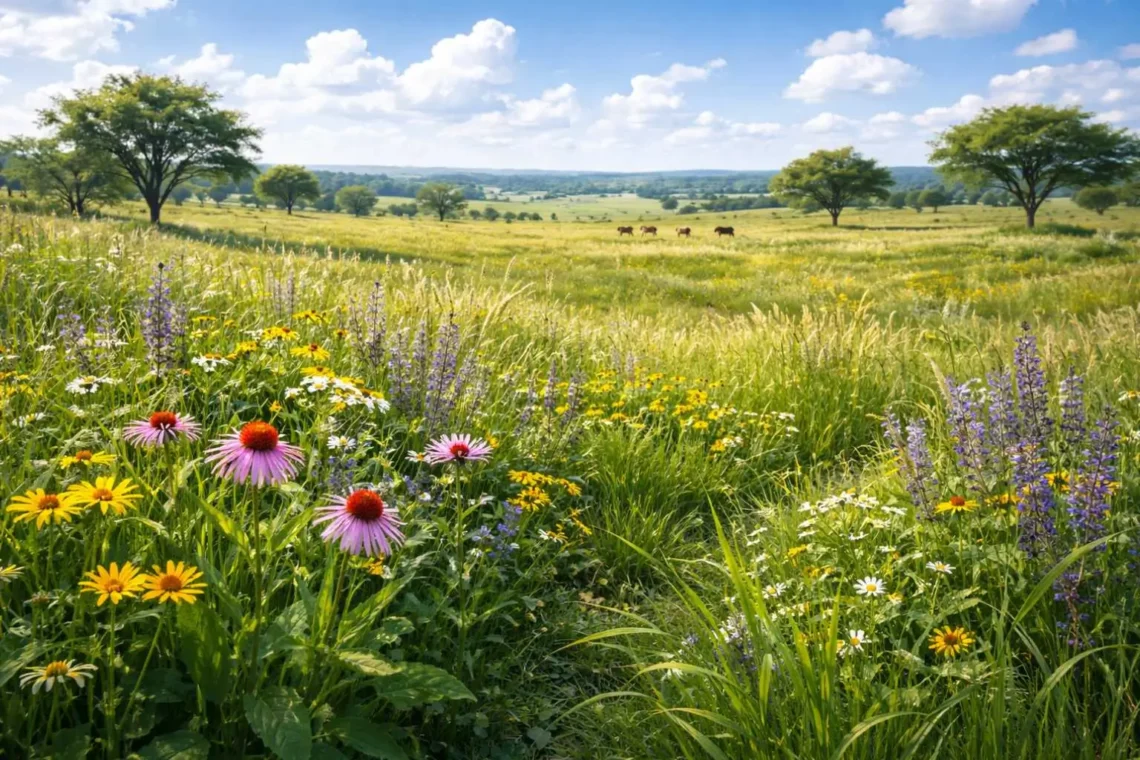
Grassland plants play a vital role in maintaining global ecosystems by supporting biodiversity, regulating climate, and sustaining food chains across vast land areas. Grasslands are one of Earth’s major biomes, covering nearly one-third of the planet’s land surface and occurring on every continent except Antarctica. These ecosystems are dominated by grasses, herbaceous plants, and a limited number of shrubs and trees adapted to open environments. Plants found in grasslands are uniquely suited to survive periodic droughts, fires, and grazing pressure. Their ecological importance lies in soil stabilization, carbon storage, and providing habitat and food for countless animals, making grassland plants essential for both environmental balance and human survival.
What Are Grassland Plants?

Grassland plants are plant species that naturally grow in grassland ecosystems where grasses dominate and tree cover is sparse. These grasslands plants are adapted to open landscapes with seasonal rainfall, strong winds, and frequent disturbances such as fire and grazing.
Plants in grassland ecosystems typically have flexible stems, extensive root systems, and rapid growth cycles. Unlike forest plants, they do not rely on shade tolerance, and unlike desert plants, they are not fully adapted to extreme aridity. Grassland plants balance moderate water availability with high exposure to sunlight, wind, and herbivores.
Types of Grasslands Where These Plants Grow
- Temperate grasslands
Found in regions with cold winters and warm summers, supporting perennial grasses and seasonal flowering plants. - Tropical grasslands (savannas)
Characterized by warm temperatures year-round, seasonal rainfall, and scattered trees. - Subtropical grasslands
Occur in transitional climates with mixed plant communities adapted to both dry and humid conditions.
Common Plants Found in Grasslands

Plants found in grasslands vary by climate and region but are dominated by grasses, low shrubs, and herbaceous flowering plants. These ecosystems support a high diversity of plant forms that grow close to the ground to resist wind, grazing, and fire.
Grasses form the structural foundation of grasslands, while shrubs and flowering plants add ecological complexity and seasonal variation.
-
Names of Grassland Plants
Grassland plants names commonly used in ecological and educational studies include buffalo grass, blue grama, switchgrass, big bluestem, needlegrass, and ryegrass. These names of grassland plants help scientists classify ecosystems, monitor biodiversity, and study plant distribution patterns across continents.
Learn more: 7+ Stunning Japanese Sweet Flag Grass Benefits You’ll Love
-
Grasslands Flowers and Flowering Plants
Grasslands flowers include species such as coneflowers, asters, lupines, and wild clovers. These flowering plants enhance visual diversity in grasslands and play a critical role in pollination. In a grassland with flowers, insects such as bees and butterflies depend on seasonal blooms for nectar, directly supporting biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Grassland Trees and Woody Plants
Trees are limited in grasslands due to low rainfall, frequent fires, and grazing pressure. Conditions favor grasses over large woody plants, preventing dense forest formation. However, some drought- and fire-tolerant trees can survive.
Examples of grassland trees include acacia, baobab, and mesquite, which are adapted to open environments with deep root systems.
Grassland Trees and Plants Together
Grassland trees and plants interact to create balanced landscapes. Trees provide shade and habitat, while grasses reduce soil erosion and support grazing animals. This coexistence maintains the open structure typical of healthy grasslands.
Plant Adaptations in Grasslands
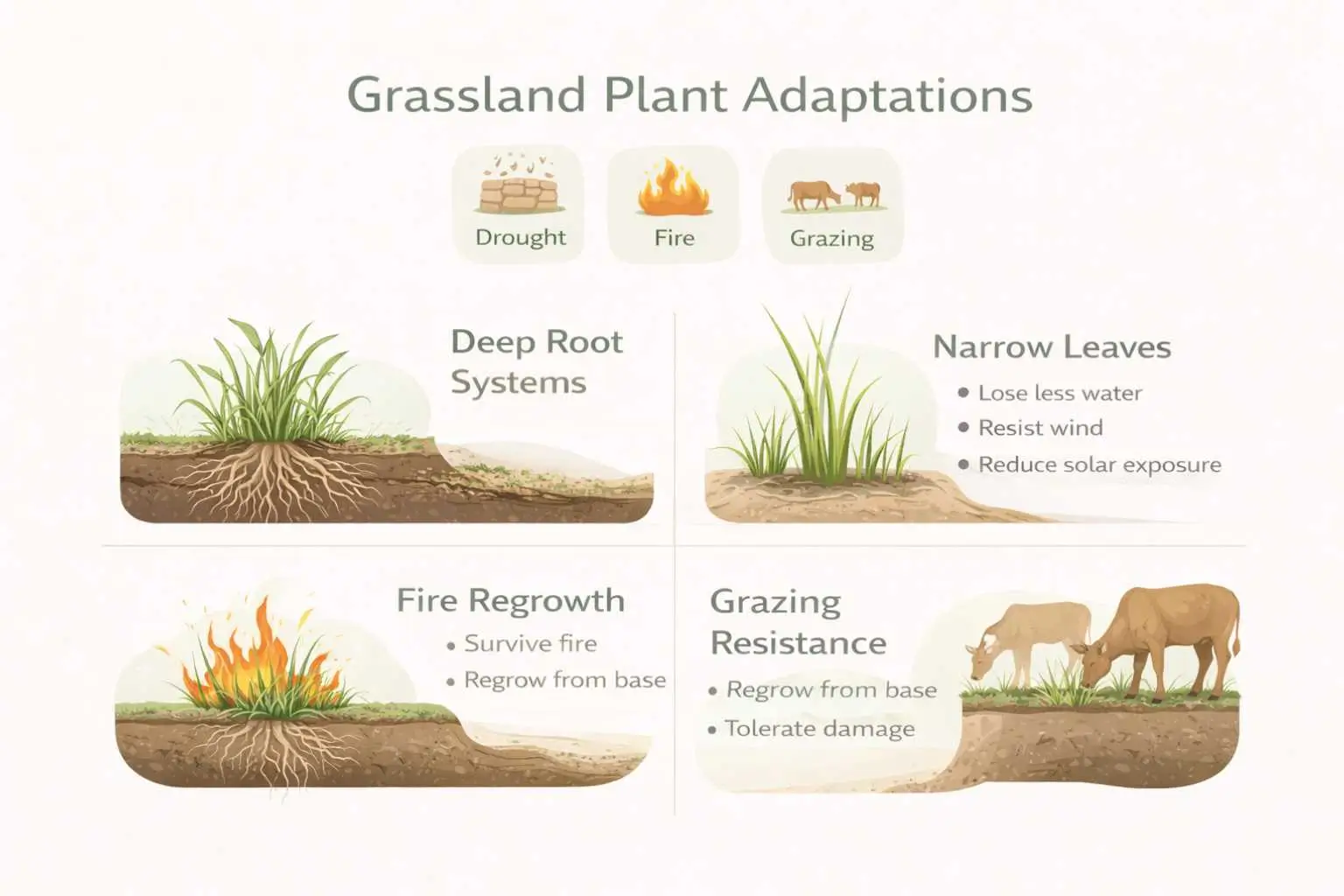
Plant adaptations in grasslands allow species to survive environmental stress, including limited water availability, fire, and herbivory. These survival strategies enable grassland plants to regenerate quickly and maintain ecosystem stability.
Structural Adaptations
- Deep root systems that access underground moisture
- Narrow leaves that reduce water loss
- Growth from the base, allowing plants to regrow after grazing or fire
These structural features are key plant adaptations in the grassland environment.
Climate-Based Adaptations
Plant adaptations in the grasslands include drought tolerance through water-efficient tissues and seasonal dormancy. Plant adaptations for grasslands also include resistance to fire and grazing, as many species can resprout quickly after damage, ensuring long-term survival.
Grassland Plants and Animals Relationship
Grassland plants form the base of the food web, directly supporting herbivores such as antelope, bison, and zebras. Predators depend on these herbivores, creating a continuous energy flow in grassland ecosystems.
Plants and Animals in Grasslands
The connection between plants and animals in grasslands is essential for ecosystem health. Vegetation provides food, nesting sites, and shelter, while animals aid in seed dispersal and nutrient cycling.
Savanna Grassland Plants
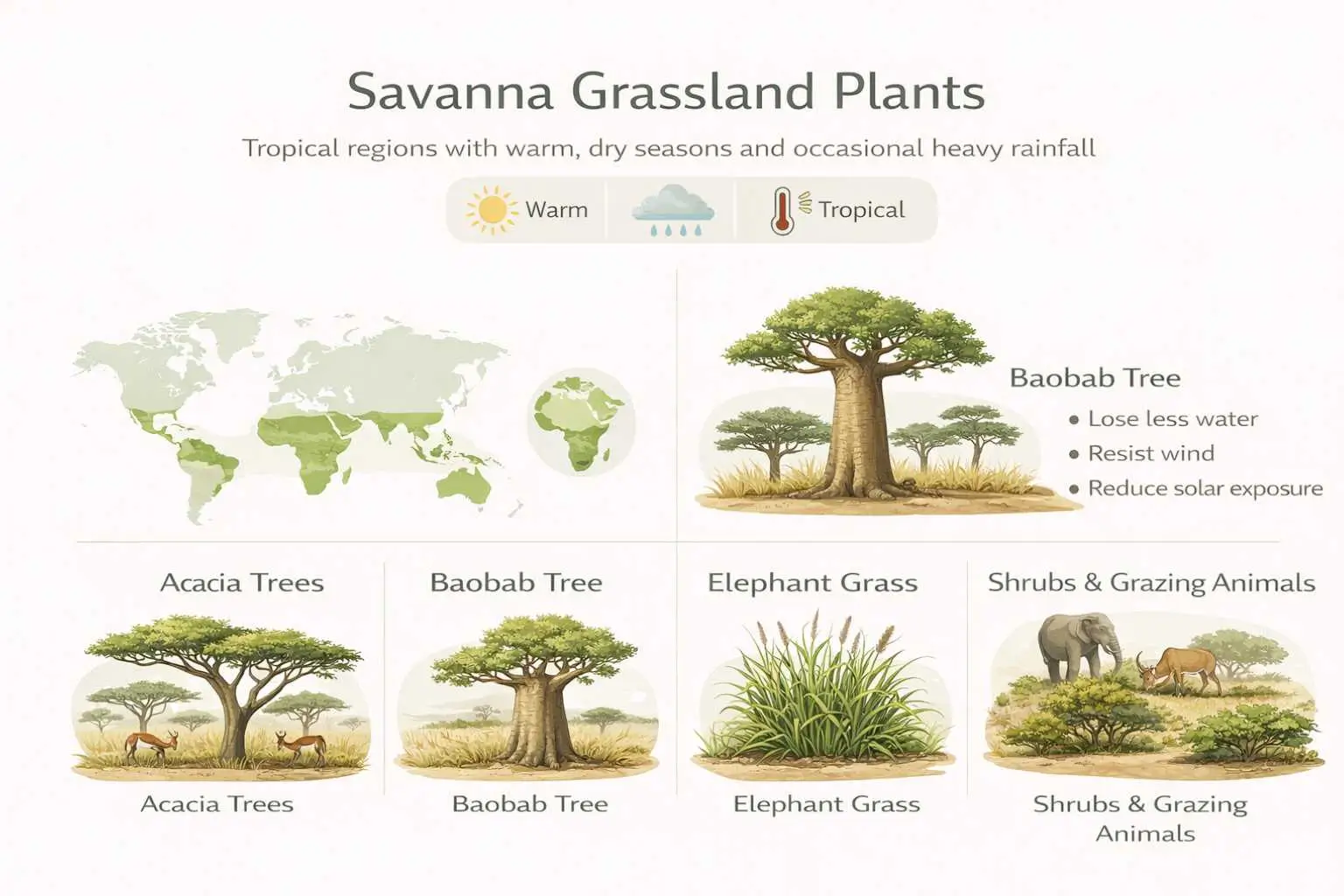
Savanna grassland plants grow in tropical grasslands characterized by scattered trees and seasonal rainfall. These ecosystems experience long dry seasons followed by intense wet periods.
Plants of the Savanna
Examples of plants of the savanna include elephant grass, acacia trees, baobab trees, and drought-resistant shrubs. Plants in the savanna are adapted to heat, fire, and grazing. Plants of savanna regions, including plants of the savanna and plants from the savanna, are essential for supporting large herbivores and maintaining open landscapes.
Importance of Grassland Plants
Grassland plants provide major environmental benefits by stabilizing soil, preventing erosion, and improving soil fertility. They contribute to climate regulation by storing carbon and influencing atmospheric cycles. Grassland plants also support biodiversity by sustaining diverse plant and animal species across large ecosystems.
Grassland Plants Names and Pictures
This section serves as a visual content placement area for grassland plants names and pictures. Including grassland plants names with images improves identification, learning, and SEO value, helping users visually connect with different species found in grasslands.
Conclusion & Call to Action
Grassland plants are fundamental to ecosystem stability, biodiversity, and climate balance. From grasses and flowers to scattered trees, these plants support complex food webs and protect the environment. Learning about grassland plants helps promote conservation and sustainable land use. Explore related ecosystems or detailed plant guides to deepen your understanding and support grassland conservation efforts.
Learn more: Aphids on Plants: 7 Proven Fixes to Save Your Plants Fast
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are grassland plants?
Grassland plants are species adapted to open ecosystems dominated by grasses, with limited tree cover and seasonal rainfall. - What plants are commonly found in grasslands?
Common plants found in grasslands include grasses, shrubs, and flowering plants such as bluestem, buffalo grass, and wildflowers. - How do plant adaptations help grassland plants survive?
Plant adaptations in grasslands help species tolerate drought, fire, and grazing through deep roots, narrow leaves, and rapid regrowth. - What is the difference between savanna plants and other grassland plants?
Savanna plants are adapted to tropical climates with seasonal rainfall and often include scattered trees, unlike temperate grasslands. - Why are grassland plants important for ecosystems and animals?
Grassland plants support food chains, prevent soil erosion, regulate climate, and provide habitat for diverse animal species.






